NXP MIMXRT1060-EVK
Overview
The i.MX RT1060 adds to the industry’s first crossover processor series and expands the i.MX RT series to three scalable families.
The i.MX RT1060 doubles the On-Chip SRAM to 1MB while keeping pin-to-pin compatibility with i.MX RT1050. This series introduces additional features ideal for real-time applications such as High-Speed GPIO, CAN FD, and synchronous parallel NAND/NOR/PSRAM controller. The i.MX RT1060 runs on the Arm® Cortex-M7® core up to 600 MHz.
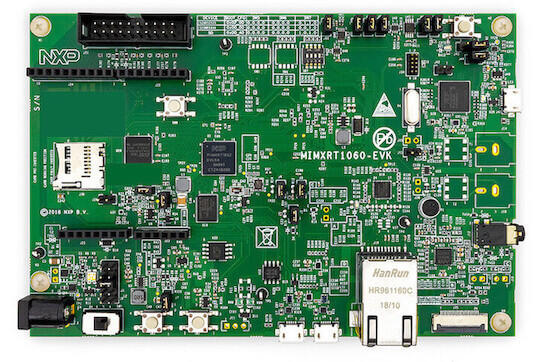
Hardware
MIMXRT1062DVL6A MCU (600 MHz, 1024 KB on-chip memory)
Memory
256 Mbit SDRAM
64 Mbit QSPI Flash
512 Mbit Hyper Flash
TF socket for SD card
Display
LCD connector
Ethernet
10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet PHY
USB
USB 2.0 OTG connector
USB 2.0 host connector
Audio
3.5 mm audio stereo headphone jack
Board-mounted microphone
Left and right speaker out connectors
Power
5 V DC jack
Debug
JTAG 20-pin connector
OpenSDA with DAPLink
Sensor
FXOS8700CQ 6-axis e-compass
CMOS camera sensor interface
Expansion port
Arduino interface
CAN bus connector
For more information about the MIMXRT1060 SoC and MIMXRT1060-EVK board, see these references:
External Memory
This platform has the following external memories:
Device |
Controller |
Status |
|---|---|---|
IS25WP064AJBLE |
SEMC |
Enabled via device configuration data block, which sets up SEMC at boot time |
IS42S16160J |
FLEXSPI |
Enabled via flash configurationn block, which sets up FLEXSPI at boot time. |
Supported Features
The mimxrt1060_evk board configuration supports the hardware features listed below. For additional features not yet supported, please also refer to the NXP MIMXRT1064-EVK , which is the superset board in NXP’s i.MX RT10xx family. NXP prioritizes enabling the superset board with NXP’s Full Platform Support for Zephyr. Therefore, the mimxrt1064_evk board may have additional features already supported, which can also be re-used on this mimxrt1060_evk board:
Interface |
Controller |
Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
NVIC |
on-chip |
nested vector interrupt controller |
SYSTICK |
on-chip |
systick |
DISPLAY |
on-chip |
eLCDIF. Tested with RK043FN02H-CT Parallel Display, and RK043FN66HS-CTG Parallel Display shields |
FLASH |
on-chip |
QSPI flash |
GPIO |
on-chip |
gpio |
SPI |
on-chip |
spi |
I2C |
on-chip |
i2c |
WATCHDOG |
on-chip |
watchdog |
SDHC |
on-chip |
disk access |
UART |
on-chip |
serial port-polling; serial port-interrupt |
ENET |
on-chip |
ethernet |
USB |
on-chip |
USB device |
CAN |
on-chip |
can |
DMA |
on-chip |
dma |
ADC |
on-chip |
adc |
SAI |
on-chip |
i2s |
GPT |
on-chip |
gpt |
TRNG |
on-chip |
entropy |
FLEXSPI |
on-chip |
flash programming |
PIT |
on-chip |
pit |
The default configuration can be found in boards/nxp/mimxrt1060_evk/mimxrt1060_evk_defconfig
Other hardware features are not currently supported by the port.
Connections and I/Os
The MIMXRT1060 SoC has five pairs of pinmux/gpio controllers.
Name |
Function |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
GPIO_AD_B0_00 |
LPSPI1_SCK |
SPI |
GPIO_AD_B0_01 |
LPSPI1_SDO |
SPI |
GPIO_AD_B0_02 |
LPSPI3_SDI/LCD_RST| SPI/LCD Display |
|
GPIO_AD_B0_03 |
LPSPI3_PCS0 |
SPI |
GPIO_AD_B0_05 |
GPIO |
SD Card |
GPIO_AD_B0_09 |
GPIO/ENET_RST |
LED |
GPIO_AD_B0_10 |
GPIO/ENET_INT |
GPIO/Ethernet |
GPIO_AD_B0_11 |
GPIO |
Touch Interrupt |
GPIO_AD_B0_12 |
LPUART1_TX |
UART Console |
GPIO_AD_B0_13 |
LPUART1_RX |
UART Console |
GPIO_AD_B1_00 |
LPI2C1_SCL |
I2C |
GPIO_AD_B1_01 |
LPI2C1_SDA |
I2C |
GPIO_AD_B1_06 |
LPUART3_TX |
UART BT HCI |
GPIO_AD_B1_07 |
LPUART3_RX |
UART BT HCI |
WAKEUP |
GPIO |
SW0 |
GPIO_B0_00 |
LCD_CLK |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_01 |
LCD_ENABLE |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_02 |
LCD_HSYNC |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_03 |
LCD_VSYNC |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_04 |
LCD_DATA00 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_05 |
LCD_DATA01 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_06 |
LCD_DATA02 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_07 |
LCD_DATA03 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_08 |
LCD_DATA04 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_09 |
LCD_DATA05 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_10 |
LCD_DATA06 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_11 |
LCD_DATA07 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_12 |
LCD_DATA08 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_13 |
LCD_DATA09 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_14 |
LCD_DATA10 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B0_15 |
LCD_DATA11 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B1_00 |
LCD_DATA12 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B1_01 |
LCD_DATA13 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B1_02 |
LCD_DATA14 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B1_03 |
LCD_DATA15 |
LCD Display |
GPIO_B1_04 |
ENET_RX_DATA00 |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_05 |
ENET_RX_DATA01 |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_06 |
ENET_RX_EN |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_07 |
ENET_TX_DATA00 |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_08 |
ENET_TX_DATA01 |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_09 |
ENET_TX_EN |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_10 |
ENET_REF_CLK |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_11 |
ENET_RX_ER |
Ethernet |
GPIO_B1_12 |
GPIO |
SD Card |
GPIO_B1_14 |
USDHC1_VSELECT |
SD Card |
GPIO_B1_15 |
BACKLIGHT_CTL |
LCD Display |
GPIO_EMC_40 |
ENET_MDC |
Ethernet |
GPIO_EMC_41 |
ENET_MDIO |
Ethernet |
GPIO_AD_B0_09 |
ENET_RST |
Ethernet |
GPIO_AD_B0_10 |
ENET_INT |
Ethernet |
GPIO_SD_B0_00 |
USDHC1_CMD/LPSPI1_SCK | SD Card/SPI |
|
GPIO_SD_B0_01 |
USDHC1_CLK/LPSPI1_PCS0 | SD Card/SPI |
|
GPIO_SD_B0_02 |
USDHC1_DATA0/LPSPI1_SDO | SD Card/SPI |
|
GPIO_SD_B0_03 |
USDHC1_DATA1/LPSPI1_SDI | SD Card/SPI |
|
GPIO_SD_B0_04 |
USDHC1_DATA2 |
SD Card |
GPIO_SD_B0_05 |
USDHC1_DATA3 |
SD Card |
GPIO_AD_B1_11 |
ADC |
ADC1 Channel 0 |
GPIO_AD_B1_10 |
ADC |
ADC1 Channel 15 |
GPIO_AD_B1_09 |
SAI1_MCLK |
I2S |
GPIO_AD_B1_12 |
SAI1_RX |
I2S |
GPIO_AD_B1_13 |
SAI1_TX |
I2S |
GPIO_AD_B1_14 |
SAI1_TX_BCLK |
I2S |
GPIO_AD_B1_15 |
SAI1_TX_SYNC |
I2S |
GPIO_AD_B1_02 |
1588_EVENT2_OUT |
1588 |
GPIO_AD_B1_03 |
1588_EVENT2_IN |
1588 |
Note
In order to use the SPI peripheral on this board, resistors R278, R279, R280 and R281 must be populated with zero ohm resistors.
System Clock
The MIMXRT1060 SoC is configured to use SysTick as the system clock source, running at 600MHz.
When power management is enabled, the 32 KHz low frequency oscillator on the board will be used as a source for the GPT timer to generate a system clock. This clock enables lower power states, at the cost of reduced resolution
Serial Port
The MIMXRT1060 SoC has eight UARTs. LPUART1 is configured for the console,
LPUART3 for the Bluetooth Host Controller Interface (BT HCI), and the
remaining are not used.
Programming and Debugging
This board supports 3 debug host tools. Please install your preferred host tool, then follow the instructions in Configuring a Debug Probe to configure the board appropriately.
J-Link Debug Host Tools (Default, Supported by NXP)
LinkServer Debug Host Tools (Supported by NXP)
pyOCD Debug Host Tools (Not Supported by NXP)
Once the host tool and board are configured, build and flash applications as usual (see Building an Application and Run an Application for more details).
Configuring a Debug Probe
Two revisions of the RT1060 EVK exist. For the RT1060 EVK, J47/J48 are the SWD isolation jumpers, J42 is the DFU mode jumper, and the 20 pin JTAG/SWD header is present on J21. For the RT1060 EVKB, J9/J10 are the SWD isolation jumpers, J12 is the DFU mode jumper, and the 20 pin JTAG/SWD header is present on J2.
A debug probe is used for both flashing and debugging the board. This board has an LPC-LINK2 Onboard Debug Probe. The default firmware present on this probe is the LPC-Link2 DAPLink Onboard Debug Probe.
Based on the host tool installed, please use the following instructions to setup your debug probe:
LinkServer Debug Host Tools: Using CMSIS-DAP with LPC-Link2 Probe
pyOCD Debug Host Tools: Using CMSIS-DAP with LPC-Link2 Probe
Using CMSIS-DAP with LPC-Link2 Probe
Follow the instructions provided at LPC-LINK2 CMSIS DAP Onboard Debug Probe to reprogram the default debug probe firmware on this board.
Ensure the SWD isolation jumpers are populated
Using J-Link with LPC-Link2 Probe
There are two options: the onboard debug circuit can be updated with Segger J-Link firmware, or a J-Link External Debug Probe can be attached to the EVK.
To update the onboard debug circuit, please do the following:
Switch the power source for the EVK to a different source than the debug USB, as the J-Link firmware does not power the EVK via the debug USB.
Follow the instructions provided at LPC-Link2 J-Link Onboard Debug Probe to reprogram the default debug probe firmware on this board.
Ensure the SWD isolation jumpers are populated.
To attach an external J-Link probe, ensure the SWD isolation jumpers are removed, then connect the probe to the external JTAG/SWD header
See Using J-Link with MIMXRT1060-EVK or MIMXRT1064-EVK or Using J-Link with MIMXRT1060-EVKB for more details.
Configuring a Console
Regardless of your choice in debug probe, we will use the OpenSDA microcontroller as a usb-to-serial adapter for the serial console. Check that jumpers J45 and J46 are on (they are on by default when boards ship from the factory) to connect UART signals to the OpenSDA microcontroller.
Connect a USB cable from your PC to J41.
Use the following settings with your serial terminal of choice (minicom, putty, etc.):
Speed: 115200
Data: 8 bits
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Using SWO
SWO can be used as a logging backend, by setting CONFIG_LOG_BACKEND_SWO=y.
Your SWO viewer should be configured with a CPU frequency of 132MHz, and
SWO frequency of 7500KHz.
Flashing
Here is an example for the Hello World application.
# From the root of the zephyr repository
west build -b mimxrt1060_evk samples/hello_world
west flash
Open a serial terminal, reset the board (press the SW9 button), and you should see the following message in the terminal:
***** Booting Zephyr OS v1.14.0-rc1 *****
Hello World! mimxrt1060_evk
Debugging
Here is an example for the Hello World application.
# From the root of the zephyr repository
west build -b mimxrt1060_evk samples/hello_world
west debug
Open a serial terminal, step through the application in your debugger, and you should see the following message in the terminal:
***** Booting Zephyr OS v1.14.0-rc1 *****
Hello World! mimxrt1060_evk
Troubleshooting
If the debug probe fails to connect with the following error, it’s possible
that the boot header in QSPI flash is invalid or corrupted. The boot header is
configured by CONFIG_NXP_IMXRT_BOOT_HEADER.
Remote debugging using :2331
Remote communication error. Target disconnected.: Connection reset by peer.
"monitor" command not supported by this target.
"monitor" command not supported by this target.
You can't do that when your target is `exec'
(gdb) Could not connect to target.
Please check power, connection and settings.
You can fix it by erasing and reprogramming the QSPI flash with the following steps:
Set the SW7 DIP switches to ON-OFF-ON-OFF to prevent booting from QSPI flash.
Reset by pressing SW9
Run
west debugorwest flashagain with a known working Zephyr application.Set the SW7 DIP switches to OFF-OFF-ON-OFF to boot from QSPI flash.
Reset by pressing SW9
If the west flash or debug commands fail, and the command hangs while executing runners.jlink, confirm the J-Link debug probe is configured, powered, and connected to the EVK properly.