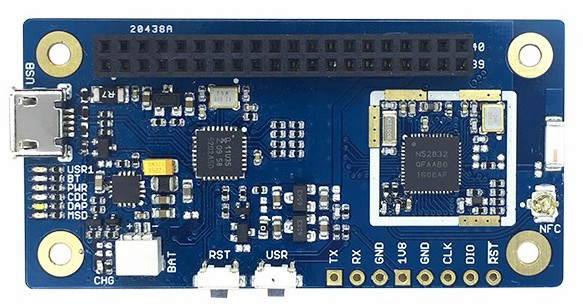
96Boards Nitrogen¶
Overview¶
Zephyr applications use the 96b_nitrogen board configuration to run on the 96Boards Nitrogen hardware. It provides support for the Nordic Semiconductor nRF52832 ARM Cortex-M4F CPU.
More information about the board can be found at the seeed BLE Nitrogen website. The Nordic Semiconductor Infocenter contains the processor’s information and the datasheet.
Hardware¶
96Boards Nitrogen provides the following hardware components:
- nRF52832 microcontroller with 512kB Flash, 64kB RAM
- ARM® 32-bit Cortex®-M4 CPU with FPU
- Bluetooth LE
- NFC
- LPC11U35 on board SWD debugger
- SWD debugger firmware
- USB to UART
- Drag and Drop firmware upgrade
- 7 LEDs
- USR1, BT, PWR, CDC, DAP, MSD, Battery charge
- SWD debug connectors
- nRF52832 SWD connector
- nRF52832 Uart connector
- On board chip antenna
- 1.8V work voltage
- 2x20pin 2.0mm pitch Low speed connector
Supported Features¶
The Zephyr 96b_nitrogen board configuration supports the following hardware features:
| Interface | Controller | Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
| NVIC | on-chip | nested vectored interrupt controller |
| RTC | on-chip | system clock |
| UART | on-chip | serial port |
| GPIO | on-chip | gpio |
| FLASH | on-chip | flash |
| RADIO | on-chip | Bluetooth |
| RTT | on-chip | console |
Other hardware features are not supported by the Zephyr kernel. See Nordic Semiconductor Infocenter for a complete list of nRF52-based board hardware features.
The default configuration can be found in the defconfig file:
boards/arm/96b_nitrogen/96b_nitrogen_defconfig
Pin Mapping¶
LED¶
- LED1 / User LED (green) = P0.29
- LED2 / BT LED (blue) = P0.28
Push buttons¶
- BUTTON = SW1 = P0.27
External Connectors¶
Low Speed Header
| PIN # | Signal Name | nRF52832 Functions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | GND |
| 3 | UART CTS | P.014 / TRACEDATA[3] |
| 5 | UART TX | P0.13 |
| 7 | UART RX | P0.15 / TRACEDATA[2] |
| 9 | UART RTS | P0.12 |
| 11 | UART TX | P0.13 |
| 13 | UART RX | P0.15 / TRACEDATA[2] |
| 15 | P0.22 | P0.22 |
| 17 | P0.20 | P0.20 |
| 19 | N/A | N/A |
| 21 | N/A | N/A |
| 23 | P0.02 | P0.02 |
| 25 | P0.04 | P0.04 |
| 27 | P0.06 | P0.06 |
| 29 | P0.08 | P0.08 |
| 31 | P0.16 | P0.16 |
| 33 | P0.18 | P0.18 |
| 35 | VCC | |
| 37 | USB5V | |
| 39 | GND | GND |
| PIN # | Signal Name | nRF52832 Functions |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | GND | GND |
| 4 | PWR BTN | |
| 6 | RST BTN | P0.21 / RESET |
| 8 | P0.26 | P0.26 |
| 10 | P0.25 | P0.25 |
| 12 | P0.24 | P0.24 |
| 14 | P0.23 | P0.23 |
| 16 | N/A | N/A |
| 18 | N/A | PC7 |
| 20 | N/A | PC9 |
| 22 | N/A | PB8 |
| 24 | P0.03 | P0.03 |
| 26 | P0.05 | P0.05 |
| 28 | P0.07 | P0.07 |
| 30 | P0.11 | P0.11 |
| 32 | P0.17 | P0.17 |
| 34 | P0.19 | P0.19 |
| 36 | NC | |
| 38 | NC | |
| 40 | GND | GND |
System Clock¶
nRF52 has two external oscillators. The frequency of the slow clock is 32.768 kHz. The frequency of the main clock is 32 MHz.
Flashing Zephyr onto 96Boards Nitrogen¶
The 96Boards Nitrogen board can be flashed via the CMSIS DAP interface, which is provided by the micro USB interface to the LPC11U35 chip.
Using the CMSIS-DAP interface, the board can be flashed via the USB storage interface (drag-and-drop) and also via pyOCD.
Installing pyOCD¶
The latest stable version of pyOCD can be installed via pip as follows:
$ pip install --pre -U pyocd
To install the latest development version (master branch), do the following:
$ pip install --pre -U git+https://github.com/mbedmicro/pyOCD.git#egg=pyOCD
You can then verify that your board is detected by pyOCD by running:
$ pyocd-flashtool -l
Common Errors¶
No connected boards¶
If you don’t use sudo when invoking pyocd-flashtool, you might get any of the following errors:
No available boards are connected
No connected boards
Error: There is no board connected.
To fix the permission issue, simply add the following udev rule for the NXP LPC1768 interface:
$ echo 'ATTR{idProduct}=="0204", ATTR{idVendor}=="0d28", MODE="0666", GROUP="plugdev"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/50-cmsis-dap.rules
Finally, unplug and plug the board again.
ValueError: The device has no langid¶
As described by pyOCD issue 259, you might get the
ValueError: The device has no langid error when not running
pyOCD as root (e.g. sudo).
To fix the above error, add the udev rule shown in the previous section and install a more recent version of pyOCD.
Flashing an Application to 96Boards Nitrogen¶
Here is an example for the Hello World application. This requires installing the pyOCD tools.
# On Linux/macOS
cd $ZEPHYR_BASE/samples/hello_world
mkdir build && cd build
# On Windows
cd %ZEPHYR_BASE%\samples\hello_world
mkdir build & cd build
# Use cmake to configure a Ninja-based build system:
cmake -GNinja -DBOARD=96b_nitrogen ..
# Now run ninja on the generated build system:
ninja
ninja flash
Run your favorite terminal program to listen for output.
$ minicom -D <tty_device> -b 115200
Replace <tty_device> with the port where the board 96Boards Nitrogen
can be found. For example, under Linux, /dev/ttyACM0.
The -b option sets baud rate ignoring the value from config.
Press the Reset button and you should see the the following message in your terminal:
Hello World! arm
Debugging with GDB¶
You can debug an application in the usual way. Here is an example for the Hello World application. This also requires pyOCD.
# On Linux/macOS
cd $ZEPHYR_BASE/samples/hello_world
# If you already made a build directory (build) and ran cmake, just 'cd build' instead.
mkdir build && cd build
# On Windows
cd %ZEPHYR_BASE%\samples\hello_world
# If you already made a build directory (build) and ran cmake, just 'cd build' instead.
mkdir build & cd build
# If you already made a build directory (build) and ran cmake, just 'cd build' instead.
# Use cmake to configure a Ninja-based build system:
cmake -GNinja -DBOARD=96b_nitrogen ..
# Now run ninja on the generated build system:
ninja debug